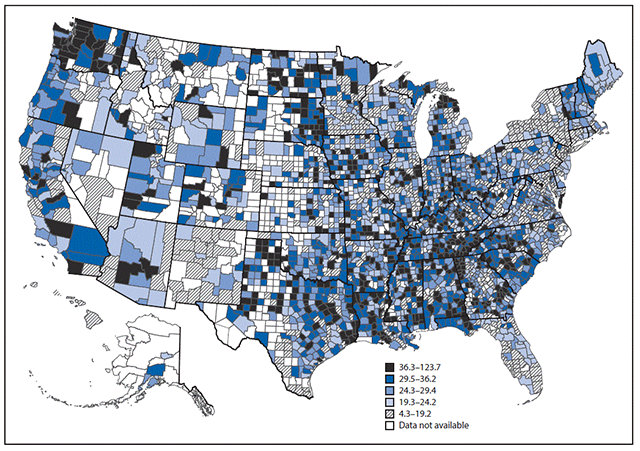
Map Shows States With the Highest Alzheimer’s Disease Deaths
Story by Marni Rose McFall
Alzheimer’s disease is a devastating neurodegenerative disorder affecting millions of Americans, and its impact varies significantly across the country.
While the disease is a nationwide concern, certain areas, particularly in the South and the Pacific Northwest, experience significantly higher mortality rates, according to data from 2022 released by the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. Factors such as healthcare access, lifestyle, and underlying health conditions may contribute to these variations.
The CDC researchers also looked at where people with Alzheimer’s were living when they died of the disease. They found that although most deaths in 2014 occurred in nursing homes or other long-term care facilities, more patients with the disease were dying at home than they were 16 years earlier.
In 1999, only 13.9 percent of people with Alzheimer’s were living at home when they died. That number rose to 24.9 percent in 2014. Another 6.1 percent died in a hospice facility.
Possible reasons for increase
“The number of Alzheimer’s deaths has increased, in part, because of a growing population of older adults,” write the CDC researchers. They also point out that the rise in deaths from Alzheimer’s disease may be the result of fewer “competing” deaths from heart disease and stroke.
In addition, Alzheimer’s is now much more likely to be correctly diagnosed — and cited on death certificates as the direct cause of death — than in past decades.
Whatever the reasons for the increase in the nation’s Alzheimer’s death rate, the growing burden of the disease on American families is clear.
“In 2015, caregivers of persons with dementia, including Alzheimer’s, provided 18.2 billion hours of unpaid assistance,” write the researchers. “These caregiving hours might correspond to increased financial costs for caregivers and decreased work productivity, as caregivers might take leave from work to ensure adequate care is provided.”
“As Alzheimer’s disease progresses, caregiving becomes very important,” explained Christopher Taylor, a CDC epidemiologist who led the study, in the released statement. “Caregivers and patients can benefit from programs that include education about Alzheimer’s disease, how to take care of themselves and their loved one, and case management to lessen the burden of care.”
“Supportive interventions can lessen the burden for caregivers and improve the quality of care for people with Alzheimer’s disease,” he added.
What Is Alzheimer’s Disease?
The National Institute on Aging defines Alzheimer‘s disease as a progressive brain disorder that gradually destroys memory, thinking skills, and the ability to perform simple tasks.

Stock image shows an elderly woman wearing a blue sweater, track pants and sneakers slowly walking in parks with a rollator walker. It is a sunny autumn day in Frederick, Maryland. Data from the CDC shows how the mortality rate of Alzheimer’s changes from state to state. Grandbrothers/Getty Images©
It is most common in people over 65, with late-onset Alzheimer’s being the predominant form. In rare cases, early-onset Alzheimer’s can occur between a person’s 30s and mid-60s. The disease is the leading cause of dementia among older adults.
Named after Dr. Alois Alzheimer, who first observed abnormal clumps (amyloid plaques) and tangled fibers (tau tangles) in the brain of a woman with memory loss and erratic behavior, these features remain key indicators of the disease today.
Alzheimer’s is marked by the buildup of plaques and tangles, as well as the loss of connections between neurons that transmit messages within the brain and to other parts of the body. The damage initially impacts areas critical to memory, such as the entorhinal cortex and hippocampus, before spreading to regions responsible for language, reasoning, and social behavior.
Over time, this widespread brain deterioration severely impairs cognitive and physical abilities, leading to the loss of independence in those affected. While scientists continue to investigate other complex brain changes that may contribute to Alzheimer’s, plaques, tangles, and neuronal damage remain central to understanding the disease. Alzheimer’s Risk Higher If Mom Had Memory Problems
Delayed REM sleep phase linked to increased Alzheimer’s risk, research finds
Why Does Washington Have A High Rate of Alzheimer’s – Search
Which State Has the Highest Alzheimer’s Mortality Rate?
Stats of the States – Alzheimer’s Disease Mortality
The top five states with the highest Alzheimer’s mortality rates are:
- Mississippi
- Washington
- Alabama
- Arkansas
- Louisiana
- Idaho
- Utah
- Georgia
- Texas
- California
What Causes the State Differences?
According to research from the University of Alabama, Alzheimer’s disease disproportionately affects the Deep South, where states like Alabama, Georgia, Louisiana, Mississippi, and South Carolina see significantly higher rates of dementia.
People born in this region have a 20–30 percent greater risk of developing Alzheimer’s or other forms of dementia, largely due to underlying health disparities. Factors such as high rates of hypertension, diabetes, obesity, and vascular disease in the region contribute to cognitive decline and increase dementia risk. These conditions are particularly prevalent among African Americans, who make up over 20 percent of the population in the Deep South, and face twice the risk of late-onset Alzheimer’s compared to other groups.
A key issue in addressing Alzheimer’s disparities is the underrepresentation of African Americans in Alzheimer’s-related research. Although African Americans make up around 10 percent of the U.S. population over 55, few clinical studies have included a proportionate number of African American participants.
The Deep South is also a hotspot for other health conditions that heighten the risk of Alzheimer’s, including cerebrovascular disease, diabetes, and obesity. The so-called “Stroke Belt” – Search and “Diabetes Belt” – Search—areas in the region where those diseases are prevalent—contribute to widespread vascular problems and cognitive decline, while obesity is linked to inflammation that could exacerbate dementia.
A spokesperson for UsAgainstAlzheimer’s said, “There are a number of comorbidities that can increase a person’s risk of developing Alzheimer’s or related dementias and controlling these can reduce a person’s risk of developing Alzheimer’s. We should be clear that hypertension and diabetes are not really “lifestyle factors” but diseases that can be treated—and they should be treated.”
“One of the things we are focused on is making sure the public knows there are things people can do to reduce their risk of Alzheimer’s. Hypertension, diabetes, social isolation, and tobacco use, to name a few, are examples of the risk factors. But people can make simple lifestyle changes to reduce their risk. Exercise, sleep, eating a healthy diet, and even wearing hearing aids if you have hearing loss are just some of the actions people can take to reduce the risk of developing Alzheimer’s.”
“Access to information and healthcare are two of the biggest challenges,” the spokesperson said.
“Working with the Centers for Disease Control, we are working very hard to reach these very communities so we can raise Alzheimer’s awareness and encourage people to talk about it. But you still have the issue of access to healthcare and adequate treatment – not only for dementia but to address the other factors that increase the risk for Black and Latino people, in particular. We need a healthcare system that works for everyone; getting there is a major priority for ‘UsAgainstAlzheimer’s.” – Search
Scientists list 12 risk factors that could lead to dementia before the age of 65
The States That Drink the Most Alcohol in America (2024) [MAP] | VinePair
Poor sleep may lead to higher risk of dementia, scientists find
Update, 17/10/24, 12:01 p.m. ET: This article was updated with comment from UsAgainstAlzheimer’s.
| Estimate of U.S. prevalence of adults aged 18 and over with any serious medical condition, as of 2018. (CDC map) |
A new report from the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention has a map showing which counties have populations with an increased risk of severe outcomes from covid-19. Many are rural, since rural populations tend to be older, more obese, and are more likely to have underlying medical conditions.
Read more here: https://www.cdc.gov/mmwr/volumes/69/wr/pdfs/mm6929a1-H.pdf from The Rural Blog https://ift.tt/2ZUVyZA Map shows which states have adults at higher risk of serious illness with covid-19 – Entrepreneur Generations
Andrew E. Budson M.D. | Psychology Today
1Alzheimer’s Disease: Pathology and Stages | Psychology Today
2Can Alzheimer’s Disease Be Diagnosed During Life? | Psychology Today
3Am I at Risk for Alzheimer’s Disease? | Psychology Today
<<<<<<<<<<<< >>>>>>>>>>>>
1 Medications to Enhance Memory | Psychology Today
2 Medications to Improve Apathy & Attention | Psychology Today
3 How to Treat Anxiety and Depression in People With Dementia | Psychology Today

